RNase P
Rfam ID: RF0009
RF00010
RF00011
RF00030
RF00373
RF02375
click into different sections:
Timeline
Timeline of Bacterial RNase P
-
1971 Discovery[1]
-
1972 Purification and properties[2]
-
1983 RNA is the catalytic subunit[3]
-
1988 Role of the protein[4]
-
1988 Secondary structure of RNA[5]
-
1991 Long-range structure in RNA[6]
-
1995 S-domain and C-domain of RNA[7]
-
1996 Catalytic core of RNA [8]
-
1997 Conserved core of RNA[9]
-
1998 Structure of the B-type RNase P protein[10]
-
2003 Structure of the A-type RNase P protein[11]
-
2003 Crystal structure of S-domain (B-type)[12]
-
2004 Crystal structure of S-domain (A-type)[13]
-
2005 Crystal structure of A-type RNase P RNA[14]
-
2005 Crystal structure of B-type RNase P RNA[15]
-
2009 Metal-binding sites in the C-domain[16]
-
2010 Cryo-EM structure of bacterial RNase P holoenzyme in complex with tRNA and the catalytic mechanism[17]
Timeline of Archaeal RNase P
-
1990 Discovery[1]
-
1991 RNA is the catalytic subunit[2]
-
1996 Secondary structure of RNA[3]
-
2001 The secondary structure of RNA contains A-type and M-type [4]
-
2002 Four archaeal RNase P protein sequences[5]
-
2003 Reconstitution of archaeal RNase P[6]
-
2006 A fifth protein subunit Ph1496p of archaeal RNase P[7]
-
2019 Cryo-EM structure of archaeal RNase P holoenzyme and catalytic mechanism[8]
Timeline of Nuclear RNase P
-
1978 Discovery [1]
-
1996 Domain structure of RNA [2]
-
1997 Secondary structure of RNA [3]
-
2000 RNA is the catalytic subunit[4]
-
2000 P3 hairpin of RNase P RNA is important[5]
-
2001 Pop1p interacts with the P3 domain is critical[6]]
-
2005 P4 is important in the catalytic reaction[7]
-
2006 Function of eukaryotic RNase P RNA[8]
-
2018 Cryo-EM structure of yeast RNase P holoenzymeand the catalytic mechanism[9]
-
2018 Cryo-EM structure of the Human RNase P holoenzyme and the catalytic mechanism.[10]
Timeline of RNase MRP
-
1987 Discovery[1]
-
2000 MRP3 hairpin of RNase MRP RNA is important[2]
-
2001 Pop1p interacts with the P3 domain is critical[3]
-
2005 P4 is important in the catalytic reaction[4]
-
2020 Cryo-EM structure of yeast RNase MRP holoenzyme[5]
-
2020 Substrate recognition mechanism of yeast RNase MRP[6]
Description
Ribonuclease (RNase) P is a ribozyme responsible for processing the 5'-leader of precursor transfer RNA (pre-tRNA) and is widely distributed in all three kingdoms of life: Archaea, Bacteria and Eucarya. RNase P is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex, which consists of a catalytic RNA and one or more protein components.
Ribonuclease mitochondrial RNA processing (RNase MRP) is a eukaryotic ribonucleoprotein (RNP) that is evolutionarily related to RNase P. RNase MRP processes precursor ribosomal RNA (pre-rRNA) by recognizing a short, loosely defined consensus sequence.
Structure and mechanism
2D representation
Secondary structure of T. maritima RNase P RNA. The crystallized T. maritima RNase P RNA consists of eighteen paired helices (P1 to P18), five universally conserved regions (CR-I to CR-V) (gray). P1/P4/P5/P6 is shown in blue, P2/P3 stems in pink, P7 and P10/P11/P12 in yellow, P8/P9 in green, P13/P14 in cyan, P15/P16/L17 in red, and P18 in orange. The crystallized RNase P RNA contains two domains, termed the catalytic (C) and specificity (S) domains, are shown.

|
3D visualisation
Crystal structure of T. maritima RNase P RNA. P1/P4/P5/P6 is shown in blue, P2/P3 stems in pink, P7 and P10/P11/P12 in yellow, P8/P9 in green, P13/P14 in cyan, P15/P16/L17 in red, and P18 in orange. This representation was generated from PDB ID: 3Q1Q at 3.8 Å resolution.
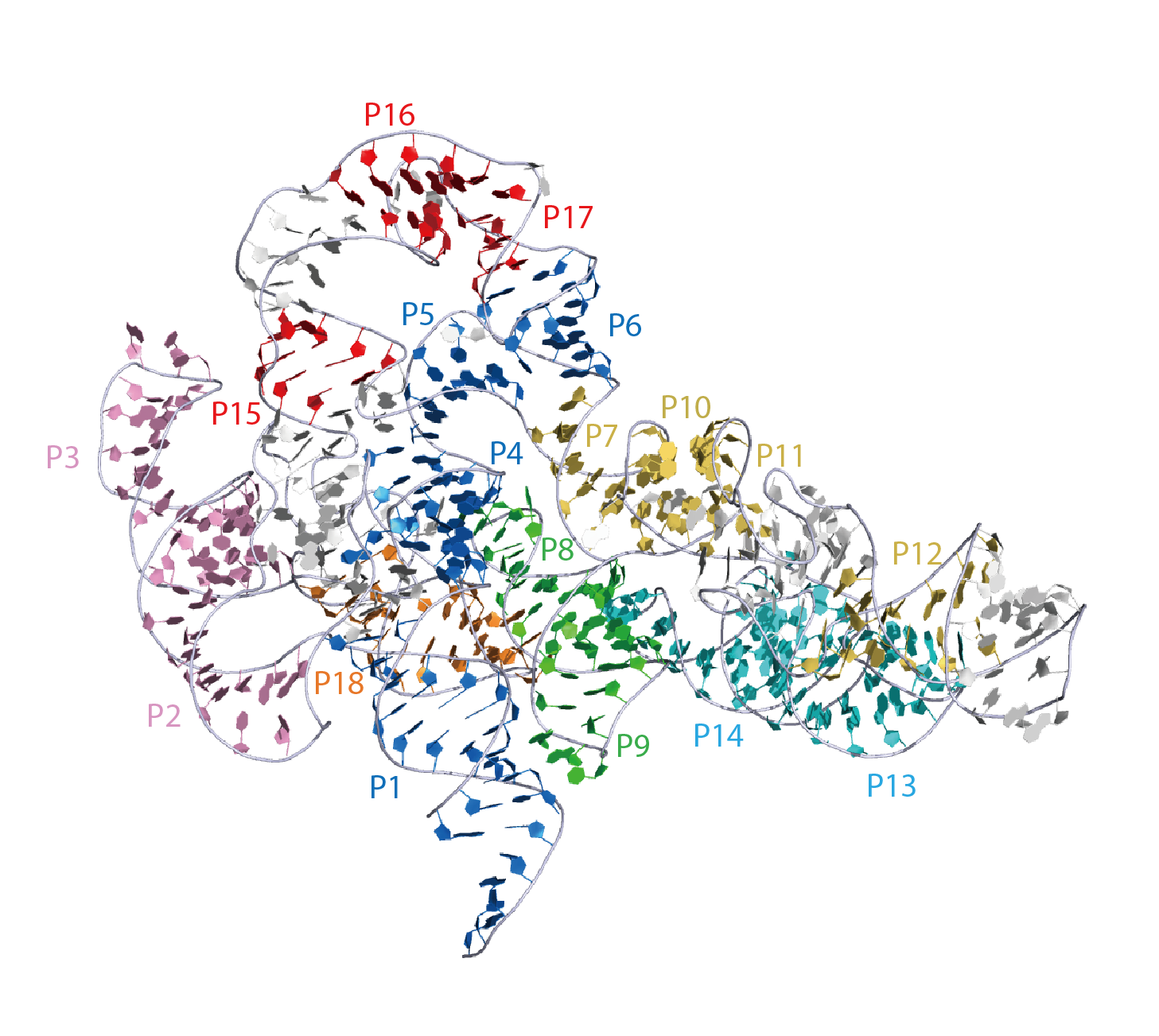 |
|
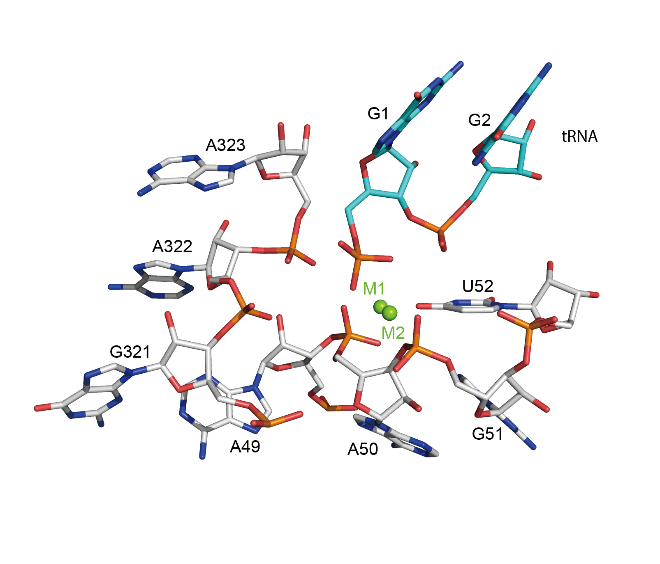
Catalytic centre
Close-up views of the catalytic centers of T. maritima RNase P (PDB: 3Q1R). Two catalytic Mg2+ ions (M1 and M2) in the active site of RNase P shown in green spheres. RNase P RNA and tRNA substrate are showed in stick representation and colored in silver and cyan, respectively.
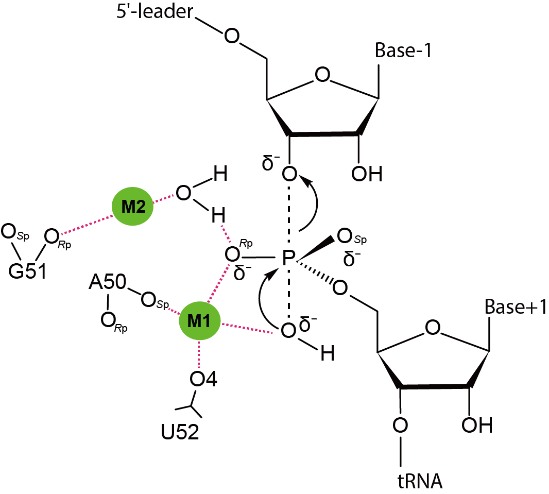
Proposed reaction mechanism for 5'-leader cleavage of pre-tRNA by RNase P. The pre-tRNA scissile phosphate is depicted in a transition state, and the interactions between catalytically important nucleotides and reactive oxygens mediated by Mg2+ions (M1 and M2) are shown as magenta dashed lines.
 |
 |
References
Bacterial RNase P
[1] Tyrosine tRNA precursor molecule polynucleotide sequence.
Altman, S. and J. D. Smith
Nat New Biol 233(36): 35-39.(1971)
[2] Purification and properties of a specific Escherichia coli ribonuclease which cleaves a tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid presursor.
Robertson, H. D., S. Altman and J. D. Smith
J Biol Chem 247(16): 5243-5251.(1972)
[3] The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme.
Guerrier-Takada, C., K. Gardiner, T. Marsh, N. Pace and S. Altman
Cell 35(3 Pt 2): 849-857.(1983)
[4] Role of the protein moiety of ribonuclease P, a ribonucleoprotein enzyme.
Reich, C., G. J. Olsen, B. Pace and N. R. Pace
Science 239(4836): 178-181.(1988)
[5] The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme.
James, B. D., G. J. Olsen, J. S. Liu and N. R. Pace
Cell 52(1): 19-26.(1988)
[6] Long-range structure in ribonuclease P RNA.
Haas, E. S., D. P. Morse, J. W. Brown, F. J. Schmidt and N. R. Pace
Science 254(5033): 853-856.(1991)
[7] Higher order folding and domain analysis of the ribozyme from Bacillus subtilis ribonuclease P.
Pan, T.
Biochemistry 34(3): 902-909.(1995)
[8] Mycoplasma fermentans simplifies our view of the catalytic core of ribonuclease P RNA.
Siegel, R. W., A. B. Banta, E. S. Haas, J. W. Brown and N. R. Pace
Rna 2(5): 452-462.(1996)
[9] Identification of the universally conserved core of ribonuclease P RNA.
Chen, J. L. and N. R. Pace
Rna 3(6): 557-560.(1997)
[10] Ribonuclease P protein structure: evolutionary origins in the translational apparatus.
Stams, T., S. Niranjanakumari, C. A. Fierke and D. W. Christianson
Science 280(5364): 752-755.(1998)
[11] High-resolution structure of RNase P protein from Thermotoga maritima.
Kazantsev, A. V., A. A. Krivenko, D. J. Harrington, R. J. Carter, S. R. Holbrook, P. D. Adams and N. R. Pace
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(13): 7497-7502.(2003)
[12] Crystal structure of the specificity domain of ribonuclease P.
Krasilnikov, A. S., X. Yang, T. Pan and A. Mondragón
Nature 421(6924): 760-764.(2003)
[13] Basis for structural diversity in homologous RNAs.
Krasilnikov, A. S., Y. Xiao, T. Pan and A. Mondragón
Science 306(5693): 104-107.
(2004)
[14] Crystal structure of the RNA component of bacterial ribonuclease P.
Torres-Larios, A., K. K. Swinger, A. S. Krasilnikov, T. Pan and A. Mondragón
Nature 437(7058): 584-587.(2005)
[15] Crystal structure of a bacterial ribonuclease P RNA.
Kazantsev, A. V., A. A. Krivenko, D. J. Harrington, S. R. Holbrook, P. D. Adams and N. R. Pace
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(38): 13392-13397.(2005)
[16] Mapping metal-binding sites in the catalytic domain of bacterial RNase P RNA.
Kazantsev, A. V., A. A. Krivenko and N. R. Pace
Rna 15(2): 266-276.(2009)
[17] Structure of a bacterial ribonuclease P holoenzyme in complex with tRNA.
Reiter, N. J., A. Osterman, A. Torres-Larios, K. K. Swinger, T. Pan and A. Mondragón
Nature 468(7325): 784-789.(2010)
Archaeal RNase P
[1] Characterization of ribonuclease P from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus.
Darr, S. C., B. Pace and N. R. Pace
J Biol Chem 265(22): 12927-12932.(1990)
[2]The RNA component of RNase P from the archaebacterium Haloferax volcanii.
Nieuwlandt, D. T., E. S. Haas and C. J. Daniels
J Biol Chem 266(9): 5689-5695.(1991)
[3] Comparative analysis of ribonuclease P RNA structure in Archaea.
Haas, E. S., D. W. Armbruster, B. M. Vucson, C. J. Daniels and J. W. Brown
Nucleic Acids Res 24(7): 1252-1259.(1996)
[4] New insight into RNase P RNA structure from comparative analysis of the archaeal RNA.
Harris, J. K., E. S. Haas, D. Williams, D. N. Frank and J. W. Brown
Rna 7(2): 220-232.(2001)
[5] Archaeal RNase P has multiple protein subunits homologous to eukaryotic nuclear RNase P proteins.
Hall, T. A. and J. W. Brown
Rna 8(3): 296-306.(2002)
[6] Reconstitution of archaeal ribonuclease P from RNA and four protein components.
Kouzuma, Y., M. Mizoguchi, H. Takagi, H. Fukuhara, M. Tsukamoto, T. Numata and M. Kimura
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306(3): 666-673.(2003)
[7] A fifth protein subunit Ph1496p elevates the optimum temperature for the ribonuclease P activity from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.
Fukuhara, H., M. Kifusa, M. Watanabe, A. Terada, T. Honda, T. Numata, Y. Kakuta and M. Kimura
Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343(3): 956-964.(2006)
[8] Cryo-electron microscopy structure of an archaeal ribonuclease P holoenzyme.
Wan, F., Q. Wang, J. Tan, M. Tan, J. Chen, S. Shi, P. Lan, J. Wu and M. Lei
Nat Commun 10(1): 2617.(2019)
Nuclear RNase P
[1] Purification and some properties of a specific nuclease which cleaves transfer RNA precursors from the posterior silk gland of Bombyx mori.
Tsutsumi, K., R. Tsutsumi-Majima and K. Shimura
J Biochem 84(1): 169-177.(1978)
[2] Domain structure of the ribozyme from eubacterial ribonuclease P.
Loria, A. and T. Pan
Rna 2(6): 551-563.(1996)
[3] Identification of the universally conserved core of ribonuclease P RNA.
Chen, J. L. and N. R. Pace
Rna 3(6): 557-560.(1997)
[4] Evidence for an RNA-based catalytic mechanism in eukaryotic nuclear ribonuclease P.
Thomas, B. C., J. Chamberlain, D. R. Engelke and P. Gegenheimer
Rna 6(4): 554-562.(2000)
[5] Functional equivalence of hairpins in the RNA subunits of RNase MRP and RNase P in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Lindahl, L., S. Fretz, N. Epps and J. M. Zengel
Rna 6(5): 653-658.(2000)
[6] An essential protein-binding domain of nuclear RNase P RNA.
Ziehler, W. A., J. Morris, F. H. Scott, C. Millikin and D. R. Engelke
Rna 7(4): 565-575.(2001)
[7] Identification and analysis of ribonuclease P and MRP RNA in a broad range of eukaryotes.
Piccinelli, P., M. A. Rosenblad and T. Samuelsson
Nucleic Acids Res 33(14): 4485-4495.(2005)
[8] Structure and function of eukaryotic Ribonuclease P RNA.
Marquez, S. M., J. L. Chen, D. Evans and N. R. Pace
Mol Cell 24(3): 445-456.(2006)
[9] Structural insight into precursor tRNA processing by yeast ribonuclease P.
Lan, P., M. Tan, Y. Zhang, S. Niu, J. Chen, S. Shi, S. Qiu, X. Wang, X. Peng, G. Cai, H. Cheng, J. Wu, G. Li and M. Lei
Science 362(6415).(2018)
[10] Cryo-EM Structure of the Human Ribonuclease P Holoenzyme.
Wu, J., S. Niu, M. Tan, C. Huang, M. Li, Y. Song, Q. Wang, J. Chen, S. Shi, P. Lan and M. Lei
Cell 175(5): 1393-1404.e1311.(2018)
RNase MRP
[1] A novel endoribonuclease cleaves at a priming site of mouse mitochondrial DNA replication.
Chang, D. D. and D. A. Clayton
Embo j 6(2): 409-417.(1987)
[2] Functional equivalence of hairpins in the RNA subunits of RNase MRP and RNase P in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Lindahl, L., S. Fretz, N. Epps and J. M. Zengel
Rna 6(5): 653-658.(2000)
[3] An essential protein-binding domain of nuclear RNase P RNA.
Ziehler, W. A., J. Morris, F. H. Scott, C. Millikin and D. R. Engelke
Rna 7(4): 565-575.(2001)
[4] Identification and analysis of ribonuclease P and MRP RNA in a broad range of eukaryotes.
Piccinelli, P., M. A. Rosenblad and T. Samuelsson
Nucleic Acids Res 33(14): 4485-4495.(2005)
[5] Cryo-EM structure of catalytic ribonucleoprotein complex RNase MRP.
Perederina, A., D. Li, H. Lee, C. Bator, I. Berezin, S. L. Hafenstein and A. S. Krasilnikov
Nat Commun 11(1): 3474.(2020)
[6]Structural insight into precursor ribosomal RNA processing by ribonuclease MRP.
Lan, P., B. Zhou, M. Tan, S. Li, M. Cao, J. Wu and M. Lei
Science 369(6504): 656-663.(2020)
 Home
Home Database
Database Research
Research About us
About us

