Ribosome
click into different sections:
Timeline
-
1975 Secondary structure of 5S RNA[1]
-
1980 A secondary structure model of bacterial 16S rRNA[2]
-
1981 Construction of 23S ribosomal RNA secondary structure model by comparing sequences[3]
-
1991 Preliminary analysis of the structure of the H. marismortui ribosomal 50 S subunit[4]
-
1992 23S ribosomal RNA may be participated in peptidyl transferase function.[5]
-
1993 NMR structure of sarcin/ricin loop in 28s rRNA[6]
-
1995 G2252 and G2251 of the 23S rRNA P-loop are important[7]
-
1995 CryoEM structure of E. coli ribosomes (25 Å)[8]
-
1998 9 Å resolution electron density map of the H. marismortui ribosome 50S subunit[9]
-
1999 G2553 is important[10]
-
1999 Structure of the ribosomal 30S subunit of T.thermophilus (5.5 Å)[11]
-
1999 Structure of the ribosomal 30S subunit of T.thermophilus (4.5 Å)[12]
-
1999 Crystal structures of the 70S ribosome functional complex (7.8 Å)[13]
-
2000 Crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit of H. marismortui (2.4 Å)[14]
-
2000 The ribosome is a ribozyme [15]
-
2000 Results are consistent with a mechanism wherein the nucleotide base of A2451 serves as a general acid base during peptide bond formation[16]
-
2000 Structure of the functionally activated small ribosomal subunit of Thermus thermophilus (3.3Å)[17]
-
2000 Crystal structure of the 30S subunit of Thermus thermophilus (3 Å)[18]
-
2001 Crystal structure of thecomplete 70S ribosome of Thermus thermophilus (5.5 Å)[19]
-
2003 A2602, U2585 are important[20]
-
2005 Structure of the 70s ribosome of E. coli (3.5Å)[21]
-
2011 Crystal structure of the 40S ribosomal subunit of Tetrahymena thermophila in complex with eIF1 (3.9 Å)[22]
-
2011 Crystal structure of the 60S ribosomal subunit of Tetrahymena thermophila in complex with eIF6 (3.5 Å)[23]
-
2011 Crystal structure of the yeast 80S ribosome (3.0 Å)[24]
-
2013 High-resolution Cryo EM structure of the Trypanosoma brucei ribosome[25]
-
2014 Cryo-EM structure of the 80S ribosome of Plasmodium falciparum (3.2 Å)[26]
-
2014 Structure of the yeast mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit (3.2 Å)[27]
-
2015 Structure of the human 80S ribosome (3.6 Å)[28]
-
2015 Structural snapshots of actively translating human ribosomes[29]
-
2016 Cryo-EM structure of the 60s ribosomal subunit of Leishmania (2.8Å)[30]
-
2016 Structure of the 80s ribosome of Leishmania (2.9Å)[31]
-
2017 Cryo-EM structure of the 60S ribosomal subunit of Plasmodium cruzi (2.5 Å)[32]
-
2017 Cryo-EM structure of the 80S ribosome of Plasmodium falciparum (3.2 Å)[33]
-
2018 Cryo-EM structure of the complete translation initiation complex from mammalian mitochondria (3.2 Å)[34]
-
2019 Late steps in bacterial translation initiation visualized using time-resolved cryo-EM[35]
-
2020 Cryo-EM structure of the RNA-rich plant mitochondrial ribosome[36]
-
2020 Cryo-EM of elongating ribosome with EF-Tu•GTP elucidates tRNA proofreading[37]
-
2020 Structural basis of mitochondrial translation (3.0 Å)[38]
-
2020 Structure of the bacterial ribosome at 2 Å resolution[39]
-
2021 Structural basis of translation termination, rescue, and recycling in mammalian mitochondria[40]
-
2022 Mechanism of mitoribosomal small subunit biogenesis and preinitiation[41]
Description
Description:Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all living cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.
Structure and mechanism
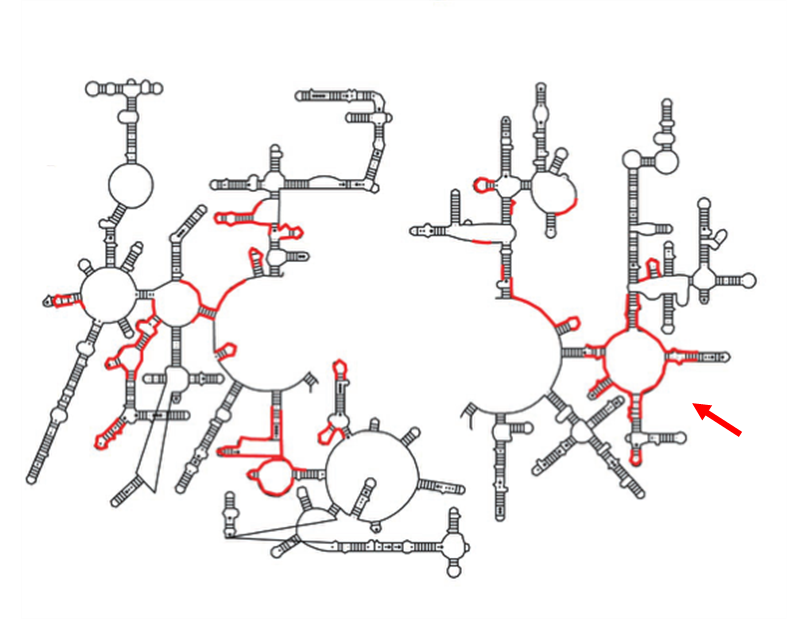
2D representation
Secondary structure schematic of 23S rRNA identifying the sequences that approach the tunnel in red (left). Secondary structure diagram of the active site region. The P-loop is connected through a large region of domain V not included in these figures (right).
 |

|
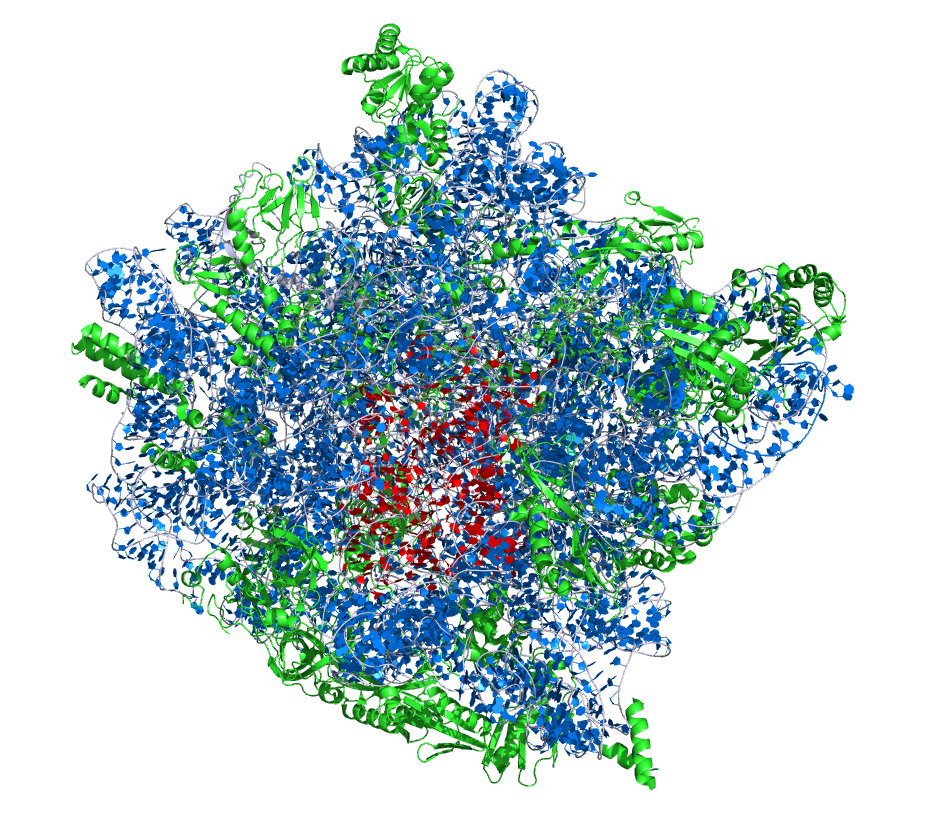
3D visualisation
The crystallographic structure of the H. marismortui large ribosomal subunit. The 23S rRNA and 5S rRNA are shown in blue and ribosomal proteins are in green. The active site region is highlighted by nucleotides of the 23S rRNA peptidyl transferase loop and shown in red. The figure was generated from the PDB ID:1JJ2 at 2.4 Å resolution (left). The crystallographic structure of the active site region (right).
 |
|
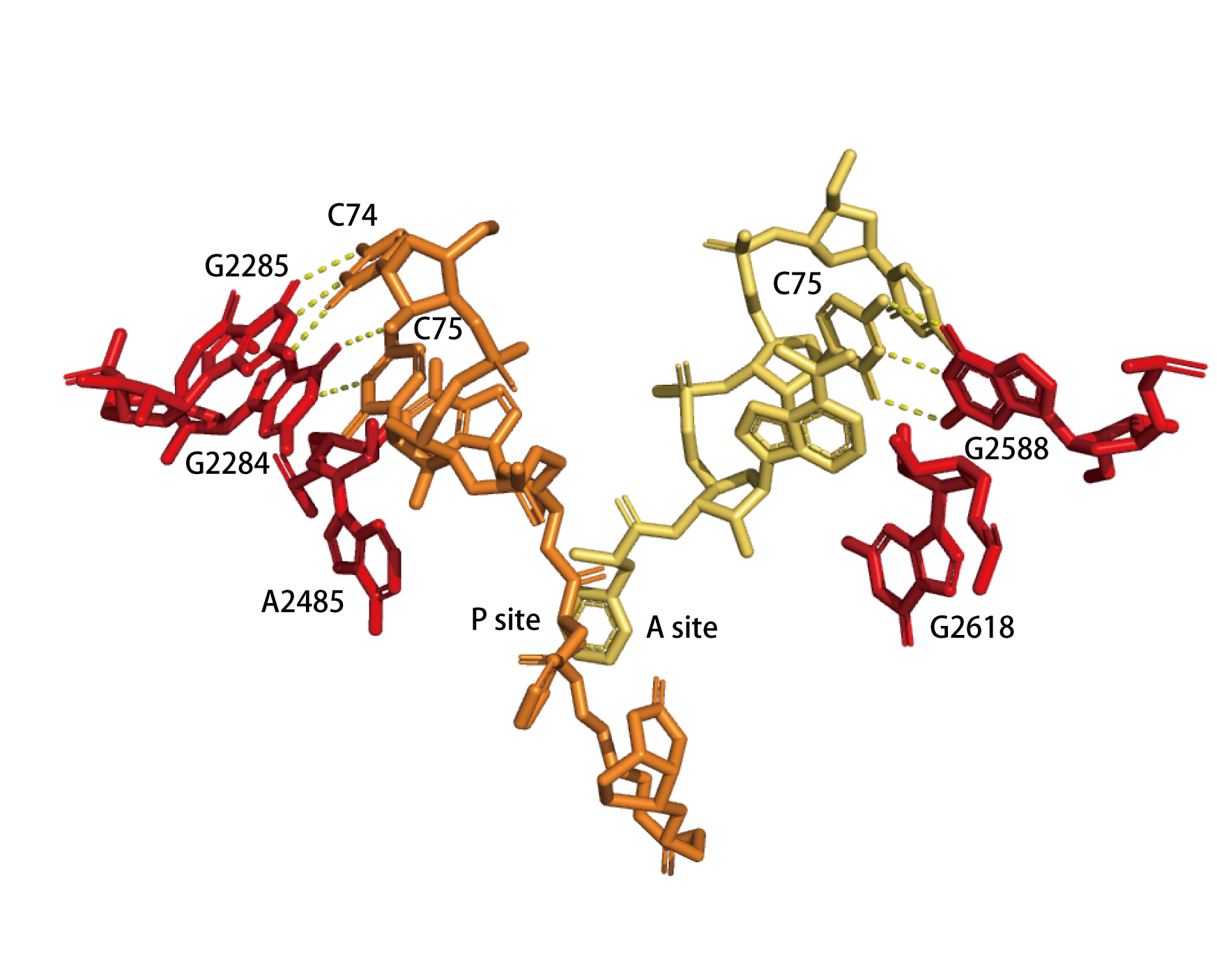
Catalytic centre
Active-site residues of 50S subunits from H. marismortui with either bound substrate (a) or a transition-state analog (b). (a)The substrate binds to the active site. The figure indicates base pairing between the cytosine residues of the tRNA analogs at the A (yelllow) and P (orange) positions and the 23S rRNA bases (red). The α-amino group of the substrate at the A position attacks the carbonyl carbon of the ester in the peptide moiety linking the substrate at the P position. (PDB ID: 1VQN) (b) Transition-state analog (TSA) bound to the peptidyl-transferase center. The hydrogen bond between the nucleophilic nitrogen and the 2’-OH of A76 at the P site is indicated. (PDB ID: 1VQP)
 |
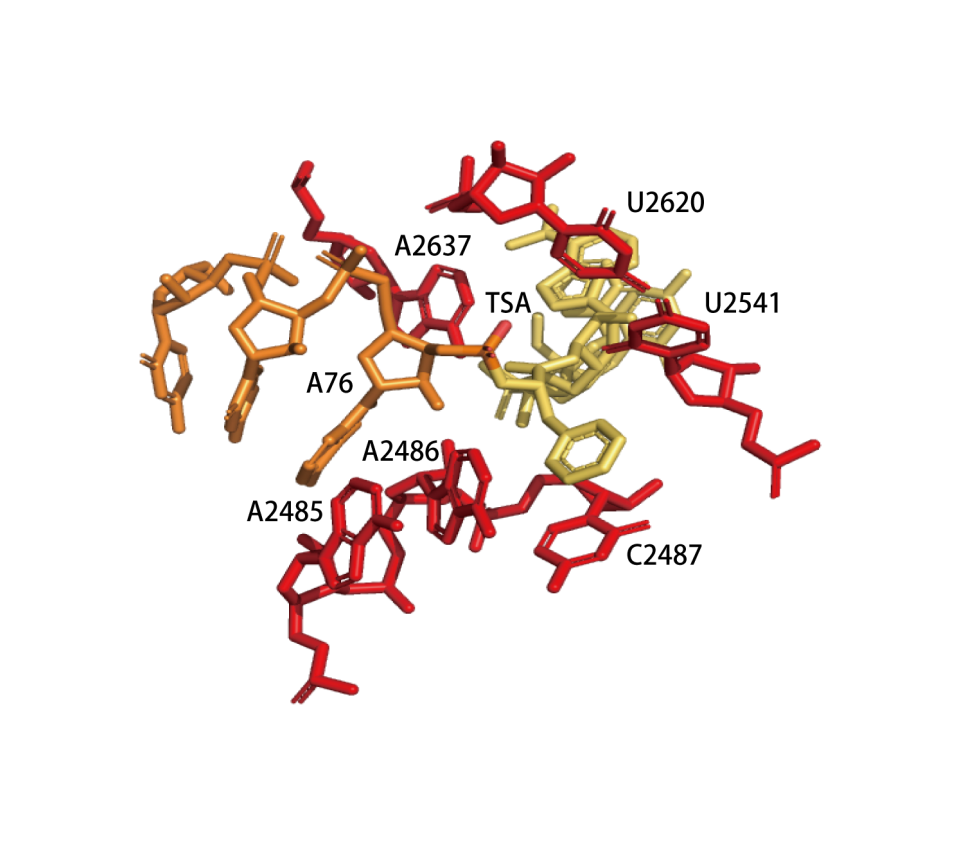 |
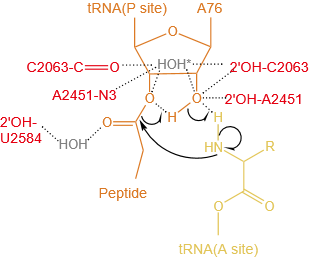
Concerted proton-shuttle mechanism. The P-site and A-site tRNA substrates are orange and yellow, respectively, ribosome residues are red, and ordered water molecules that stabilize the developing charges are gray. The attack of the α-NH2 group on the ester carbon results in a six-membered transition state, in which the 2'-OH group of the A-site A76 ribose moiety donates its proton to the adjacent 3'oxygen while simultaneously receiving one of the amino protons. Alternatively, the water molecule (*) might be used for a proton shuttle.
 |
References
[1] 5S RNA secondary structure.
Fox, G. E. and C. R. Woese
Nature 256(5517): 505-7.(1975)
[2] Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence.
Woese, C. R., L. J. Magrum, R. Gupta, R. B. Siegel, D. A. Stahl, J. Kop, N. Crawford, J. Brosius, R. Gutell, J. J. Hogan and H. F. Noller
Nucleic Acids Res 8 (10): 2275-93.(1980)
[3] Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA.
Noller, H. F., J. Kop, V. Wheaton, J. Brosius, R. R. Gutell, A. M. Kopylov, F. Dohme, W. Herr, D. A. Stahl, R. Gupta and C. R. Waese
Nucleic Acids Res 9 (22): 6167-89.(1981)
[4] Characterization and preliminary attempts for derivatization of crystals of large ribosomal subunits from Haloarcula marismortui diffracting to 3 A resolution.
von Bohlen, K., I. Makowski, H. A. Hansen, H. Bartels, Z. Berkovitch-Yellin, A. Zaytzev-Bashan, S. Meyer, C. Paulke, F. Franceschi and A. Yonath
J Mol Biol 222 (1): 11-5.(1991)
[5] Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures.
Noller, H. F., V. Hoffarth and L. Zimniak
Science 256 (5062): 1416-9.(1992)
[6] The conformation of the sarcin/ricin loop from 28S ribosomal RNA.
Szewczak, A. A., P. B. Moore, Y. L. Chang and I. G. Wool
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90 (20): 9581-5.(1993)
[7] A base pair between tRNA and 23S rRNA in the peptidyl transferase centre of the ribosome.
Samaha, R. R., R. Green and H. F. Noller
Nature 377 (6547): 309-14.(1995)
[8] A model of protein synthesis based on cryo-electron microscopy of the E. coli ribosome.
Frank, J., J. Zhu, P. Penczek, Y. Li, S. Srivastava, A. Verschoor, M. Radermacher, R. Grassucci, R. K. Lata and R. K. Agrawal
Nature 376 (6539): 441-4.(1995)
[9] A 9 A resolution X-ray crystallographic map of the large ribosomal subunit.
Ban, N., B. Freeborn, P. Nissen, P. Penczek, R. A. Grassucci, R. Sweet, J. Frank, P. B. Moore and T. A. Steitz
Cell 93 (7): 1105-15.(1998)
[10] Base-pairing between 23S rRNA and tRNA in the ribosomal A site.
Kim, D. F. and R. Green
Mol Cell 4(5): 859-64.(1999)
[11] Structure of a bacterial 30S ribosomal subunit at 5.5 A resolution.
Clemons, W. J., J. L. May, B. T. Wimberly, J. P. McCutcheon, M. S. Capel and V. Ramakrishnan
Nature 400 (6747): 833-40.(1999)
[12] The small ribosomal subunit from Thermus thermophilus at 4.5 A resolution: pattern fittings and the identification of a functional site.
Tocilj, A., F. Schlunzen, D. Janell, M. Gluhmann, H. A. Hansen, J. Harms, A. Bashan, H. Bartels, I. Agmon, F. Franceschi and A. Yonath
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96 (25): 14252-7.(1999)
[13] X-ray crystal structures of 70S ribosome functional complexes.
Cate, J. H., M. M. Yusupov, G. Z. Yusupova, T. N. Earnest and H. F. Noller
Science 285 (5436): 2095-104.(1999)
[14] The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution.
Ban, N., P. Nissen, J. Hansen, P. B. Moore and T. A. Steitz
Science 289 (5481): 905-20.(2000)
[15] The structural basis of ribosome activity in peptide bond synthesis.
Nissen, P., J. Hansen, N. Ban, P. B. Moore and T. A. Steitz
Science 289 (5481): 920-30.(2000)
[16] A single adenosine with a neutral pKa in the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center.
Muth, G. W., L. Ortoleva-Donnelly and S. A. Strobel
Science 289 (5481): 947-50.(2000)
[17] Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution.
Schluenzen, F., A. Tocilj, R. Zarivach, J. Harms, M. Gluehmann, D. Janell, A. Bashan, H. Bartels, I. Agmon, F. Franceschi and A. Yonath
Cell 102 (5): 615-23.(2000)
[18] Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit.
Wimberly, B. T., D. E. Brodersen, W. M. Clemons, Jr., R. J. Morgan-Warren, A. P. Carter, C. Vonrhein, T. Hartsch and V. Ramakrishnan
Nature 407(6802): 327-339.(2000)
[19] Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 A resolution.
Yusupov, M. M., G. Z. Yusupova, A. Baucom, K. Lieberman, T. N. Earnest, J. H. Cate and H. F. Noller
Science 292 (5518): 883-96.(2001)
[20] Structural basis of the ribosomal machinery for peptide bond formation, translocation, and nascent chain progression.
Bashan, A., I. Agmon, R. Zarivach, F. Schluenzen, J. Harms, R. Berisio, H. Bartels, F. Franceschi, T. Auerbach, H. A. Hansen, E. Kossoy, M. Kessler and A. Yonath
Mol Cell 11 (1): 91-102.(2003)
[21] Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 A resolution.
Schuwirth, B. S., M. A. Borovinskaya, C. W. Hau, W. Zhang, A. Vila-Sanjurjo, J. M. Holton and J. H. Cate
Science 310 (5749): 827-34.(2005)
[22] Crystal structure of the eukaryotic 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with initiation factor 1.
Rabl, J., M. Leibundgut, S. F. Ataide, A. Haag and N. Ban
Science 331 (6018): 730-6.(2011)
[23] Crystal structure of the eukaryotic 60S ribosomal subunit in complex with initiation factor 6.
Klinge, S., F. Voigts-Hoffmann, M. Leibundgut, S. Arpagaus and N. Ban
Science 334 (6058): 941-8.(2011)
[24] The structure of the eukaryotic ribosome at 3.0 A resolution.
Ben-Shem, A., D. L. N. Garreau, S. Melnikov, L. Jenner, G. Yusupova and M. Yusupov
Science 334 (6062): 1524-9.(2011)
[25] High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Trypanosoma brucei ribosome.
Hashem, Y., A. des Georges, J. Fu, S. N. Buss, F. Jossinet, A. Jobe, Q. Zhang, H. Y. Liao, R. A. Grassucci, C. Bajaj, E. Westhof, S. Madison-Antenucci and J. Frank
Nature 494 (7437): 385-9.(2013)
[26] Cryo-EM structure of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine.
Wong, W., X. C. Bai, A. Brown, I. S. Fernandez, E. Hanssen, M. Condron, Y. H. Tan, J. Baum and S. H. Scheres
Elife 3.(2014)
[27] Structure of the yeast mitochondrial large ribosomal subunit.
Amunts, A., A. Brown, X. C. Bai, J. L. Llacer, T. Hussain, P. Emsley, F. Long, G. Murshudov, S. Scheres and V. Ramakrishnan
Science 343 (6178): 1485-1489.(2014)
[28] Structure of the human 80S ribosome.
Khatter, H., A. G. Myasnikov, S. K. Natchiar and B. P. Klaholz
Nature 520 (7549): 640-5.(2015)
[29] Structural snapshots of actively translating human ribosomes.
Behrmann, E., J. Loerke, T. V. Budkevich, K. Yamamoto, A. Schmidt, P. A. Penczek, M. R. Vos, J. Burger, T. Mielke, P. Scheerer and C. M. Spahn
Cell 161 (4): 845-57.(2015)
[30] 2.8-A Cryo-EM Structure of the Large Ribosomal Subunit from the Eukaryotic Parasite Leishmania.
Shalev-Benami, M., Y. Zhang, D. Matzov, Y. Halfon, A. Zackay, H. Rozenberg, E. Zimmerman, A. Bashan, C. L. Jaffe, A. Yonath and G. Skiniotis
Cell Rep 16 (2): 288-294.(2016)
[31] Structures and stabilization of kinetoplastid-specific split rRNAs revealed by comparing leishmanial and human ribosomes.
Zhang, X., M. Lai, W. Chang, I. Yu, K. Ding, J. Mrazek, H. L. Ng, O. O. Yang, D. A. Maslov and Z. H. Zhou
Nat Commun 7: 13223.(2016)
[32] Determination of the ribosome structure to a resolution of 2.5 A by single-particle cryo-EM.
Liu, Z., C. Gutierrez-Vargas, J. Wei, R. A. Grassucci, M. Sun, N. Espina, S. Madison-Antenucci, L. Tong and J. Frank
Protein Sci 26 (1): 82-92.(2017)
[33] Mefloquine targets the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome to inhibit protein synthesis.
Wong, W., X. C. Bai, B. E. Sleebs, T. Triglia, A. Brown, J. K. Thompson, K. E. Jackson, E. Hanssen, D. S. Marapana, I. S. Fernandez, S. A. Ralph, A. F. Cowman, S. Scheres and J. Baum
Nat Microbiol 2: 17031.(2017)
[34] Unique features of mammalian mitochondrial translation initiation revealed by cryo-EM.
Kummer, E., M. Leibundgut, O. Rackham, R. G. Lee, D. Boehringer, A. Filipovska and N. Ban
Nature 560 (7717): 263-267.(2018)
[35] Late steps in bacterial translation initiation visualized using time-resolved cryo-EM.
Kaledhonkar, S., Z. Fu, K. Caban, W. Li, B. Chen, M. Sun, R. J. Gonzalez and J. Frank
Nature 570 (7761): 400-404.(2019)
[36] Cryo-EM structure of the RNA-rich plant mitochondrial ribosome.
Waltz, F., H. Soufari, A. Bochler, P. Giege and Y. Hashem
Nat Plants 6 (4): 377-383.(2020)
[37] Cryo-EM of elongating ribosome with EF-Tu•GTP elucidates tRNA proofreading.
Loveland, A. B., G. Demo and A. A. Korostelev
Nature 584 (7822): 640-645.(2020)
[38] Structural basis of mitochondrial translation.
Aibara, S., V. Singh, A. Modelska and A. Amunts
Elife 9.(2020)
[39] Structure of the bacterial ribosome at 2 A resolution.
Watson, Z. L., F. R. Ward, R. Meheust, O. Ad, A. Schepartz, J. F. Banfield and J. H. Cate
Elife 9.(2020)
[40] Structural basis of translation termination, rescue, and recycling in mammalian mitochondria.
Kummer, E., K. N. Schubert, T. Schoenhut, A. Scaiola and N. Ban
Mol Cell 81 (12): 2566-2582.e6.(2021)
[41] Mechanism of mitoribosomal small subunit biogenesis and preinitiation.
Itoh, Y., A. Khawaja, I. Laptev, M. Cipullo, I. Atanassov, P. Sergiev, J. Rorbach and A. Amunts
Nature 606 (7914): 603-608.(2022)
 Home
Home Database
Database Research
Research About us
About us

